Install Calico on non-cluster hosts and VMs
Big picture
Secure hosts and virtual machines (VMs) running outside of Kubernetes by installing Calico Enterprise.
Value
Calico Enterprise can also be used to protect hosts and VMs running outside of a Kubernetes cluster. In many cases, these are applications and workloads that cannot be easily containerized. Calico Enterprise lets you protect and gain visibility into these non-cluster hosts and use the same robust Calico network policy that you use for pods.
Concepts
Non-cluster hosts and host endpoints
A non-cluster host or VM is a computer that is running an application that is not part of a Kubernetes cluster. Calico Enterprise enables you to protect these hosts and VMs using the same Calico network policy that you use for workloads running inside a Kubernetes cluster. It also generates flow logs that provide visibility into the communication that host or VM is having with other endpoints in your environment.
In the following diagram, a Kubernetes cluster is running Calico Enterprise with networking (for pod-to-pod communication) and network policy; the non-cluster host uses Calico network policy for host protection and to generate flow logs for observability.
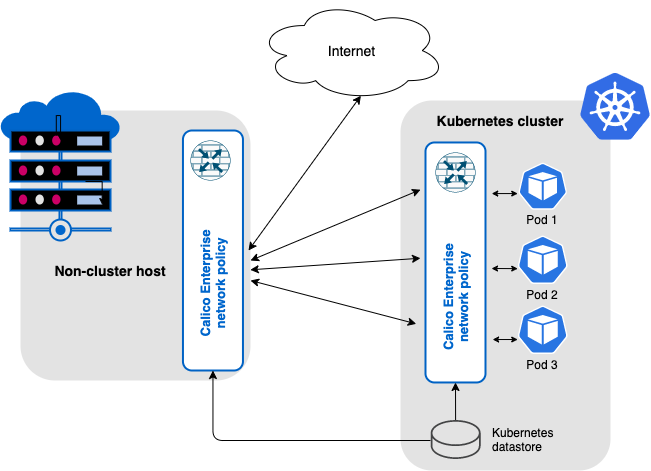
For non-cluster hosts and VMs, you can secure host interfaces using host endpoints. Host endpoints can have labels that work the same as labels on pods/workload endpoints in Kubernetes. The advantage is that you can write network policy rules to apply to both workload endpoints and host endpoints using label selectors; where each selector can refer to the either type (or be a mix of the two). For example, you can easily write a global policy that applies to every host, VM, or pod that is running Calico.
To learn how to restrict traffic to/from hosts and VMs using Calico network policy, see Protect hosts and VMs.
Before you begin
Required
-
Kubernetes API datastore is up and running and is accessible from the host
If Calico Enterprise is installed on a cluster, you already have a datastore.
-
Non-cluster host or VM meets Calico Enterprise system requirements
Ensure that your node OS includes the
ipsetandconntrackkernel dependencies.
How to
Set up your Kubernetes cluster to work with a non-cluster host or VM
-
Create a
NonClusterHostcustom resource.This resource enables the cluster-side ingestion endpoint to receive logs from non-cluster hosts. It also provides a dedicated Typha deployment to manage communication between the non-cluster host agent and Typha. To ensure proper operation, verify that the non-cluster hosts or VMs have network connectivity to your Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl create -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: NonClusterHost
metadata:
name: tigera-secure
spec:
endpoint: <https://domain-or-ip-address:port>
typhaEndpoint: <domain-or-ip-address:port>
EOFField Description Accepted Values Schema endpoint Required. Location of the log ingestion point for non-cluster hosts. Any HTTPS URL with a domain name and a port number string typhaEndpoint Required. Location of the Typha endpoint for non-cluster host agent and Typha communication. If you are using an ingress controller or an external load balancer, ensure it is configured to allow TCP Layer 4 passthrough. This is required for non-cluster host agent to establish a mutual TLS (mTLS) connection to the cluster. Any IP address or domain name with a port number string Wait until the Tigera Manager and non-cluster Typha deployments reach the Available status before proceeding to the next step.
-
Create a
kubeconfigfile for your non-cluster host or VM:calicoctl nonclusterhost generate-config [--namespace=<namespace>] [--serviceaccount=<service-account>] [--certfile=<certificate-file>] > kubeconfigParameter Description Default Values namespace Optional. The namespace where the service account for non-cluster hosts resides. calico-system serviceaccount Optional. The service account used by non-cluster hosts to authenticate and securely access the cluster. tigera-noncluster-host certfile Optional. Path to the file containing the PEM-encoded authority certificates. Use this option if you are providing your own TLS certificates for Calico Enterprise Manager. If not specified, the Tigera root CA certificate will be used by default. -
Create a
HostEndpointresource for each non-cluster host or VM. ThenodeandexpectedIPsfields are required to match the hostname and the expected interface IP addresses.
Set up your non-cluster host or VM
-
Configure the Calico Enterprise repository.
curl -sfL https://downloads.tigera.io/ee/rpms/v3.22/calico_enterprise.repo -o /etc/yum.repos.d/calico-enterprise.repoOnly Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 and 9 x86-64 operating systems are supported in this version of Calico Enterprise.
-
Install Calico node and fluent-bit log forwarder packages.
-
Use
dnfto install thecalico-nodeandcalico-fluent-bitpackages:dnf install calico-node calico-fluent-bit
-
-
Copy the
kubeconfigcreated in cluster setup step 2 to host folder/etc/calico/kubeconfig. -
Start Calico node and log forwarder.
systemctl enable --now calico-node.service
systemctl enable --now calico-fluent-bit.serviceYou can configure the Calico node by tuning the environment variables defined in the
/etc/calico/calico-node/calico-node.envfile. For more information, see the Felix configuration reference.
Configure high availability mode
High availability (HA) mode helps protect workloads running on hosts and VMs by providing an automated disaster recovery setup. It operates with two Kubernetes clusters: an active cluster and a passive cluster that remains synchronized and ready to take over if the active cluster becomes unavailable.
For HA mode to function correctly, a correctly configured load balancer (LB) is required to switch traffic between clusters during failover and failback events. The LB must detect failures, redirect traffic to the passive cluster, and restore traffic to the active cluster once it is healthy. Without a proper configuration, HA mode will not work as expected.
Your hosts or VMs are inherently HA-ready once you completed the setup steps. They automatically connect to the appropriate cluster. To enable HA mode, system administrators must perform the following steps:
- Deploy and maintain both clusters: Provision and manage both the active and passive Kubernetes clusters.
- Synchronize resources: Keep all relevant resources (such as network policies, configurations, and non-cluser host resources) synchronized from the active cluster to the passive cluster.
- Configure domain names: Use domain names (not static IP addresses) for log ingestion and Typha endpoints in the
NonClusterHostresource. - Replicate secrets: Copy the
tigera-ca-privatesecret from the active cluster to the passive cluster under thetigera-operatornamespace. After copying, verify that all Calico components in the passive cluster are running and healthy.